CAUTION: I happen to mention this idea of installing a DHIS2 instance using WSL to @bobj, and he doesn’t recommend it. However, I did this for developer/experimental purposes (as I’m still learning DHIS2, myself). Thank you so much!
Installing a local DHIS2 Debian instance on Windows 10 is fairly easy and after meeting the requirements, all one needs to do is follow the official DHIS2 Docker guide (with minor changes that are explained at the end of this post); therefore, to get started make sure you have the following requirements:
Requirements:
WINDOWS 10
There are two main things that need to be configured in your Windows 10. The first is to make sure that you are using the minimum version and build number. According to Microsoft:
- For x64 systems: Version 1903 or higher, with Build 18362 or higher.
- For ARM64 systems: Version 2004 or higher, with Build 19041 or higher.
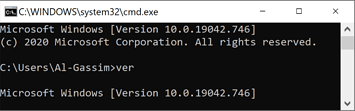
To know your version and build number, using CMD enter:
ver
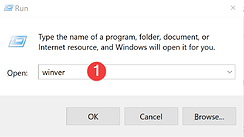
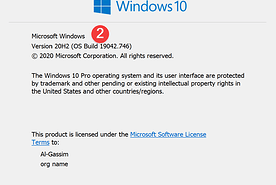
or by using Windows key + R then type winver:
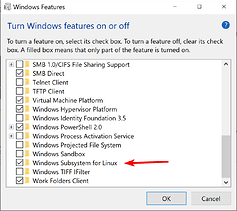
Second, make sure you enable Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) feature. Either by searching for “Turn Windows features on or off” in the start menu:
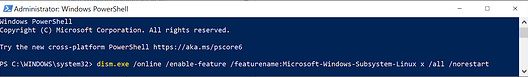
Or you can enable WSL by entering the following script in Powershell as Administrator:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux x /all /norestart
Don’t restart yet so you can Update to WSL2.
Windows Subsystem for Linux
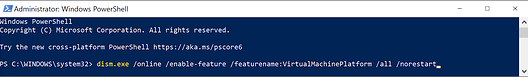
The required version of Windows Subsystem for Linux is WSL2, which means you’ll have to update WSL. For the update to be successful, you’re going to have to enable the virtual machine feature. To enable the virtual machine platform on Windows 10, open Powershell as administrator and enter the following script:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
Update to WSL2
To update you’re going to have to download the update package from Microsoft’s website: click to download update for x64 machines, or if you are using an ARM64 machine, click here to download update for ARM64 machines
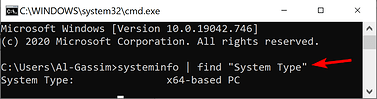
To know what kind of machine you are using, open CMD and enter:
systeminfo | find "System Type"
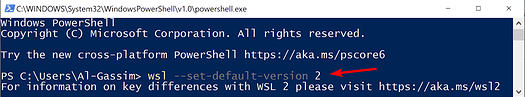
Set WSL2 as your default version
To choose your default WSL version, start Powershell as Administrator and enter:
wsl --set-default-version 2
Install Linux Debian
Although it is possible to install other linux distributions, I’ve chosen Debian because it is the one used in the official DHIS2 Docker install guide.
Click here to go to Microsoft Store and install Debian
You’ll also find a good instruction there:
To keep your Debian environment up-to-date please use the following commands:
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt dist-upgrade
Docker for Desktop
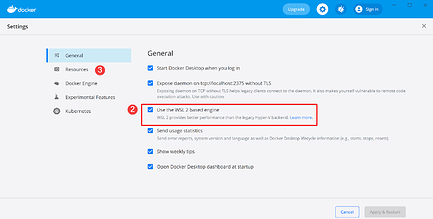
Even though we are not going to be using DHIS2 on Windows 10; however, Docker for Desktop enables integration with WSL. First, download Docker for Desktop in your Windows 10, click here. Second, after downloading Docker for Desktop, open the main window, click on settings, and make sure the following settings are enabled.
- Use the WSL 2 based engine
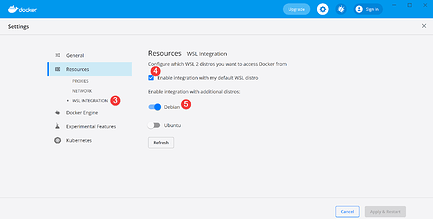
- Enable integration with my default WSL distro
- Enable Debian
After completing all the requirements above, now you are ready to follow the official DHIS2 Docker User Guide. First open your Debian terminal from the start menu:
You’re going to start by creating a default UNIX user account, and make sure you enter a new password that you can remember because it is going to be the root password for your account and you’re going to need it during the installation.
If you want to know your version number you can type:
cat /etc/os-release
Open the DHIS2 Docker Guide (click here), all commands in the guide should work, but when you get to the command systemctl because of the way WSL functions, we can’t use systemctl to start docker instead we use the command service. For example, instead of using “sudo systemctl start docker” we’re going to use “sudo service docker start.” However, do use “sudo systemctl enable docker” because it works.
All other steps should work fine until you get to the Install D2 CLI section there is a minor change that you need to make. Instead of using tee, we’re going to use nano to edit the files we want to append into. For example, use “nano ~/.config/d2/config.js” then add to the file everything after <<EOF and before the EOF at the end of the tee command used in the guide.
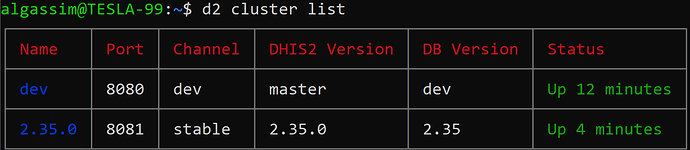
Finally when you get to the command before the last: d2 cluster up dev
If you run it and it says: Couldn’t connect to Docker daemon at http+docker://localhost - is it running?
Then make sure that the Docker for Desktop software in Windows 10 is open and in the WSL terminal run the command:
sudo service docker start
Finally just as it has been written in the Developers Guide page “Getting Started with DHIS2,” you’re going to do the following:
From the WSL terminal, start up DHIS2 and seed the database
d2 cluster up 2.38.0 --db-version 2.38 --seed
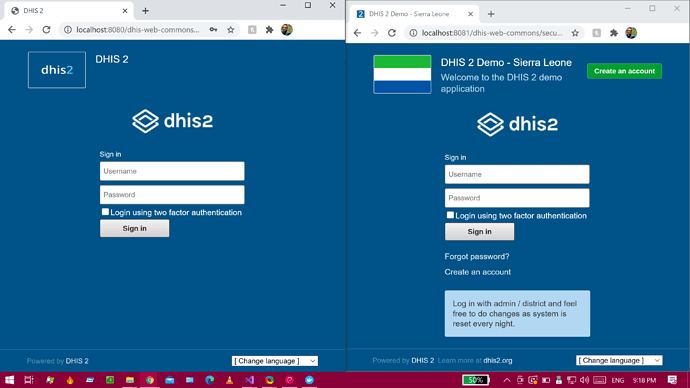
From the browser in Windows 10, navigate to http://localhost:8080
It should work fine unless you’ve installed a software that’s using the port 8080!
Sign in as admin (username) and district (password). Now you can use this instance in Windows 10 and still benefit from all the documentation, guides, and services that have been set for Debian.